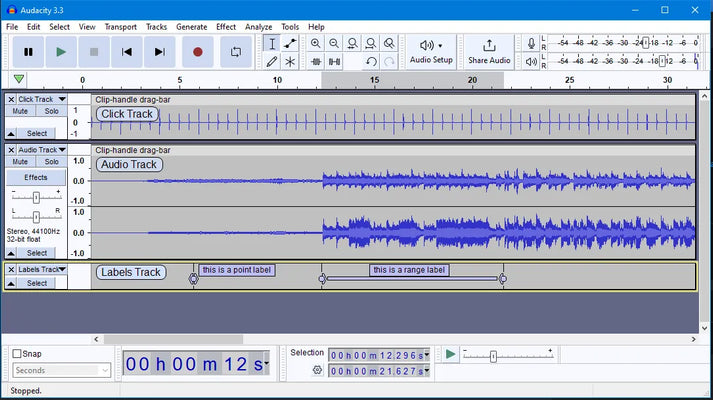
Examples Of Mastering
Overview
Definition of mastering
Mastering is the final step in the music production process that involves preparing a recording for distribution. It is a crucial stage where the audio is optimized and enhanced to achieve a polished and professional sound. Mastering involves various techniques such as equalization, compression, and stereo imaging to ensure the music's overall balance, clarity, and depth. Mastering aims to make the music sound consistent, cohesive, and ready for different playback systems. It bridges the creative process and the final product, ensuring the music translates well across other platforms and formats.
Importance of mastering
Mastering is a crucial step in music production that ensures the final mix sounds polished and professional. It involves applying various techniques and tools to enhance the overall sound quality, balance the frequencies, and optimize the dynamics. Mastering helps to achieve a cohesive and consistent sound across different playback systems and platforms. It also adds depth, clarity, and punch to the music, making it more enjoyable for the listeners. Without proper mastering, a well-produced track may lack commercial appeal and may not stand out among the competition. Therefore, investing time and effort into mastering is essential for any musician or producer striving for professional sound quality.
Process of mastering
Mastering involves several steps to ensure the final audio product is of the highest quality. These steps include:
- Editing: This removes any unwanted noise, clicks, or pops from the audio.
- Equalization: Adjusting the frequency balance of the audio to enhance clarity and tonal balance.
- Compression: Controlling the dynamic range of the audio to ensure a consistent volume level.
- Stereo Imaging: Manipulating the stereo width and depth of the audio to create a balanced and immersive soundstage.
By carefully following these steps, mastering engineers can bring out the best in the audio and make it sound professional and polished.
Techniques for Mastering
Equalization
Equalization is a fundamental technique in the mastering process that allows audio engineers to shape the frequency response of a track. By adjusting the levels of different frequencies, EQ can enhance a mix's clarity, balance, and overall tonal quality. Whether removing unwanted frequencies, boosting certain elements, or creating a sense of depth, mastering engineers utilize various EQ techniques to achieve the desired sonic impact. Some standard EQ tools used in mastering include parametric EQs, graphic EQs, and linear-phase EQs. The key is to apply EQ judiciously, considering the music's genre, style, and intended listening environment.
Compression
Compression is a crucial technique in the mastering process. It helps to control the dynamic range of audio, ensuring that softer parts are brought up in volume, and louder parts are tamed. Multiband compression is a popular approach allowing more precise control over different frequency bands. Comp compression makes the audio more cohesive and consistent, enhancing its overall impact. Additionally, parallel compression can add depth and punch to the mix. Overall, compression is essential for achieving a polished and professional sound in mastering.
Stereo Imaging
Stereo imaging is used in audio mastering to create a comprehensive and immersive soundstage. It involves manipulating the stereo field of a mix to enhance the perception of width, depth, and placement of instruments and vocals. Panorama, reverb, and delay effects are commonly used to achieve this. By carefully adjusting the placement of elements within the stereo field, engineers can create a sense of balance and separation, resulting in a more engaging and immersive listening experience.
Tools for Mastering
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs)
Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs) are essential tools for mastering audio. They provide a platform for editing, arranging, and processing audio files. Some popular DAWs include Pro Tools, Logic Pro, and Ableton Live. These software programs offer many features and capabilities, allowing mastering engineers to fine-tune the audio to achieve the desired sound. DAWs also support using mastering plugins that enhance the audio quality and provide additional control over the mastering process. Additionally, DAWs allow for comparing the mastered audio with reference tracks, helping engineers achieve a balanced and professional sound. Overall, DAWs play a crucial role in mastering workflow, enabling engineers to apply various techniques and achieve exceptional results.
Mastering Plugins
Mastering plugins is an essential tool for achieving professional sound quality in the mastering process. These plugins offer various features and effects that allow engineers to shape and enhance the audio. Some popular mastering plugins include Izotope Ozone, Waves L3 Multimaximizer, and FabFilter Pro-MB. These plugins provide powerful equalization, compression, and stereo imaging capabilities, allowing engineers to fine-tune the audio and achieve a balanced and polished sound. Additionally, mastering plugins often include metering tools that help engineers analyze and monitor the audio levels and frequencies. By using these plugins effectively, mastering engineers can bring out the best in a mix and create a final master ready for distribution and playback.
Reference Tracks
Reference tracks are previously mastered songs used as a benchmark during the mastering process. These tracks guide the achievement of the desired sonic quality and ensure that the final master sounds competitive with professional releases. By comparing the reference tracks' frequency balance, dynamics, and overall sound with the mastered mix, engineers can make informed decisions on adjustments to achieve the desired results. Choosing reference tracks that are stylistically similar to the mix being worked on is essential, as this provides a more accurate reference point. Additionally, reference tracks can help identify any issues or areas for improvement in the mix, allowing for targeted adjustments during the mastering process.
Conclusion
Benefits of mastering
Mastering is an essential step in the music production that offers several benefits. First, it enhances the overall sound quality of the music by balancing the frequencies and dynamics. Second, it ensures consistency and coherence across different tracks of an album, creating a unified listening experience. Third, mastering optimizes the sound for other playback systems, providing the music sounds great on various devices and platforms. Lastly, it adds the final polish and professional touch to the music, preparing it for distribution and release. Overall, mastering plays a crucial role in maximizing the potential of a recording and elevating it to its full sonic potential.
Tips for mastering
When it comes to mastering, a few tips can help you achieve the best results. First, listening critically to your mix and identifying any areas that need improvement is essential. Next, balance the levels of your tracks to ensure a cohesive and polished sound. Additionally, use EQ to enhance the tonal balance and apply compression to control dynamics. Lastly, consider using stereo imaging techniques to create a comprehensive and immersive soundstage. Following these tips can take your mastering skills to the next level.
Final thoughts
In conclusion, mastering is a crucial step in the music production process. It involves equalization, compression, and stereo imaging to enhance sound quality and ensure that the music translates well across different playback systems. The tools used in mastering, including Digital Audio Workstations (DAWs), mastering plugins, and reference tracks, play a vital role in achieving professional-level results. You can benefit from improved clarity, balance, and dynamics by mastering your tracks and making your music stand out in a competitive industry. To master effectively, it is essential to have a good understanding of the mastering process and to continuously refine your skills. With dedication and practice, you can master mastering and take your music to new heights.